Product Description
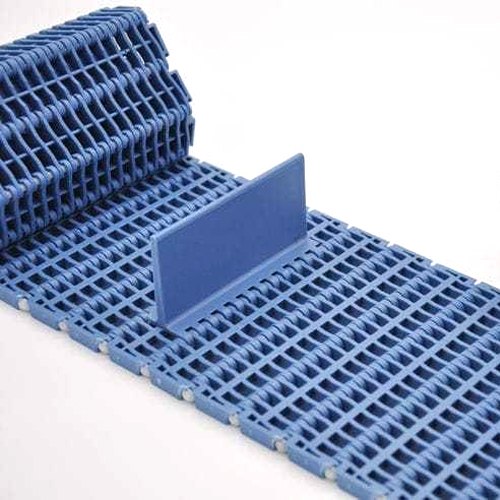
1000 Series Plastic Modular Conveyor Belt for manufacturing
Advantages:
1 This modular conveyor belt are convenient to assembly and maintain
2. This modular conveyor belt can bear High mechanical strength
3. This modular conveyor belt has Excellent product handling performance
4. This modular conveyor belt are wear resistance and Oil Resistant
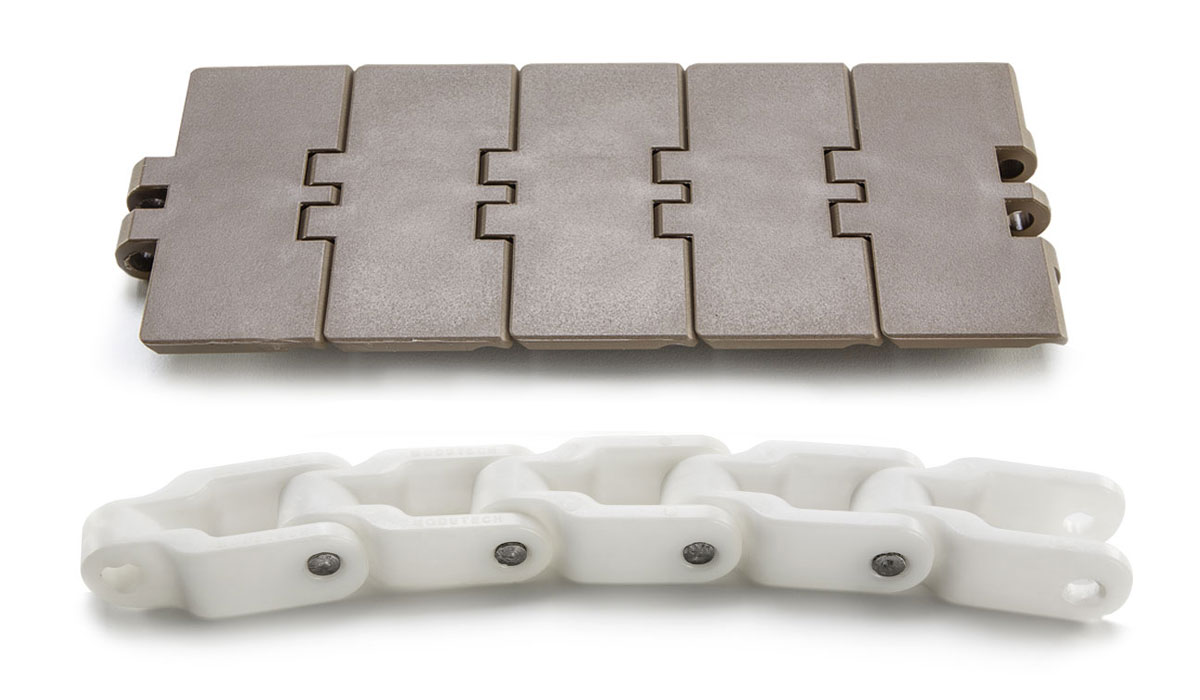
5. We are professional conveyor system manufacturer,our product line contain: modular belt, slat top chain, conveyor spare parts, conveyor system.
6. We can provide good after-sale service.
7. Every products can be customized
Application :
Specifications:
| Belt type | Pitch(mm) | Material | Belt Weight kg/m2 |
Working load | Backflex radius |
| 1000-A | 25.4 | POM | 6.5 | 22000 | 25 |
| PP | 4.25 | 11000 | |||
| PE | 4.6 | 5000 |
Product display:
Exhibitions:
Our workshop:
Package delivery:
Company Introduction:
Xihu (West Lake) Dis. Xihu (West Lake) Dis. Industrial Co., Ltd., founded in 1998, is located in HangZhou. The company covers a total area of 14000 square meters. It is a high-tech enterprise integrating scientific research and development, engineering design, production and installation, and commissioning services.It is a set of independent research and development, production, processing, sales as 1 of the automation equipment and machinery manufacturers.
If you order from us, we are sure that you will be greatly satisfied with our products and the most competitive price.We are mainly majored in Conveyor Equipments for nearly 20 years so you can be relieved for our products. We are very looking forward to receive your any enquiries or orders. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | 1000 |
|---|---|
| Material: | Metal |
| Inside Material: | Plastic |
| Feature: | Oil-Resistant, Acid And Alkali Resistant, Tear-Resistant, Heat-Resistant, Cold-Resistant, Wear-Resistant |
| Tensile Strength: | Strong |
| Backflex Radius: | 25mm |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
How do modular belts contribute to reducing friction and energy consumption in conveyor systems?
Modular belts play a significant role in reducing friction and energy consumption in conveyor systems. Here’s an in-depth explanation:
In traditional conveyor belt systems, friction between the belt and the conveyor components can result in energy losses and increased power requirements. Modular belts offer several features that help minimize friction and reduce energy consumption in conveyor systems.
- Low Coefficient of Friction:
Modular belts are engineered with materials that have a low coefficient of friction, meaning they have a reduced tendency to generate resistance or stickiness when in contact with other surfaces. This property allows for smoother movement of the belt along the conveyor system, resulting in less friction and reduced energy consumption. The low coefficient of friction also contributes to improved product flow and reduced product damage during conveying.
- Specialized Surface Patterns:
Modular belts often feature specialized surface patterns or textures that further reduce friction and improve belt performance. These patterns can include raised ribs, dimples, or microstructures that create air gaps or channels between the belt and the conveyed product. These air gaps act as a cushion, reducing surface contact and friction between the belt and the product. By minimizing frictional resistance, modular belts allow for smoother product movement and require less energy to drive the conveyor system.
- Efficient Sprocket Engagement:
Modular belts utilize sprockets to drive and guide the belt along the conveyor system. The design and engagement of the sprockets play a crucial role in reducing friction and energy consumption. Modern modular belts feature optimized sprocket engagement, where the sprocket teeth are designed to match the shape and pitch of the belt modules precisely. This precise engagement ensures minimal slippage and friction between the sprocket and the belt, resulting in efficient power transmission and reduced energy losses.
- Precise Belt Tracking:
Accurate belt tracking is essential for minimizing friction and energy consumption in conveyor systems. Modular belts are designed to maintain stable and precise tracking, reducing the risk of belt misalignment or rubbing against the conveyor components. This precise tracking minimizes unnecessary friction and wear, ensuring optimal belt performance and energy efficiency. Some modular belt systems incorporate automatic tracking technologies, such as sensors or tracking devices, to continually monitor and adjust the belt position, further enhancing tracking accuracy and reducing energy losses.
- Reduced Belt Tension Requirements:
Modular belts generally require lower tension compared to traditional conveyor belts. The low tension requirements contribute to reduced friction and energy consumption. Lower belt tension results in less strain on the conveyor components, such as bearings and drives, reducing frictional resistance and power requirements. Additionally, reduced tension helps extend the lifespan of the belt and the conveyor system, as it minimizes stress and wear on the components.
By incorporating low friction materials, specialized surface patterns, efficient sprocket engagement, precise belt tracking, and lower tension requirements, modular belts contribute to reducing friction and energy consumption in conveyor systems. These features improve overall operational efficiency, reduce power costs, and promote sustainability by minimizing energy waste.

What factors should be considered when selecting modular belts for different industrial applications?
When selecting modular belts for different industrial applications, several factors should be taken into consideration. Choosing the right modular belt requires evaluating the specific requirements of the application and matching them with the characteristics and capabilities of the belt. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Product Characteristics:
The nature of the products being conveyed is an important factor in modular belt selection. Consider the size, weight, shape, and surface properties of the products. For example, if conveying small items or products with irregular shapes, modular belts with smaller module sizes or specialized inserts may be required to ensure proper grip and stability. For heavy or bulky products, belts with higher load-carrying capacities and robust construction may be necessary.
- Operating Environment:
The operating environment plays a significant role in modular belt selection. Consider factors such as temperature, humidity, presence of liquids or chemicals, and exposure to abrasion or impact. Some modular belts are specifically designed to withstand extreme temperatures or harsh chemical environments. For applications where frequent washdowns are required, belts with high resistance to water and cleaning agents are essential. Additionally, if the application involves abrasive materials or heavy impact, belts with reinforced or wear-resistant modules should be considered.
- Conveyor Configuration:
The layout and configuration of the conveyor system should be considered when selecting a modular belt. Evaluate factors such as the presence of curves, inclines or declines, and the need for merging or diverting products. Modular belts offer flexibility and adaptability to different conveyor configurations, but it’s important to select a belt that can smoothly navigate the desired layout without causing product damage or operational issues. Belts with the appropriate module flexibility, pitch, and turning radius should be chosen for the specific conveyor configuration.
- Required Conveyor Performance:
Define the desired performance characteristics of the conveyor system. Consider factors such as speed, acceleration, and deceleration requirements. Modular belts have different capabilities regarding maximum speed and acceleration, and selecting a belt that can meet the performance demands of the application is crucial. Additionally, if the application requires precise indexing, positioning, or accumulation, modular belts with integrated features such as indexing modules or low back-pressure accumulation systems should be considered.
- Maintenance and Cleanability:
Assess the maintenance and cleanability requirements of the modular belt. Consider factors such as ease of cleaning, resistance to contaminants, and the ability to perform routine maintenance tasks. Modular belts with smooth and non-porous surfaces are easier to clean and resistant to bacterial growth. Belts that allow for easy access and module removal simplify maintenance activities, such as cleaning under the belt or replacing damaged modules. Considering the maintenance and cleanability features of the belt can contribute to overall operational efficiency and hygiene in industries with strict sanitation requirements.
- Industry Regulations and Standards:
Ensure that the selected modular belt meets relevant industry regulations and standards. Different industries, such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and electronics, have specific requirements for material handling equipment. Compliance with regulations related to food safety, hygiene, electrical safety, and chemical resistance may be necessary. Look for modular belts that are certified or compliant with industry-specific standards to ensure they meet the necessary requirements and ensure product quality and safety.
- Budget and Total Cost of Ownership:
Consider the budget and the total cost of ownership over the belt’s lifespan. While upfront costs are important, it’s essential to evaluate the long-term durability, reliability, and maintenance requirements of the modular belt. A belt that offers extended service life, minimal downtime, and low maintenance needs may result in lower overall costs and higher operational efficiency in the long run.
By carefully considering these factors, it becomes possible to select a modular belt that is well-suited for the specific industrial application, ensuring optimal performance, longevity, and cost-effectiveness.

How do modular belts differ from traditional conveyor belts in terms of design and functionality?
In terms of design and functionality, modular belts differ from traditional conveyor belts in several key ways. These differences contribute to the unique advantages and capabilities of modular belts in industrial applications. Here’s a detailed comparison:
- Design:
Traditional conveyor belts are typically made of a continuous loop of material, such as rubber or fabric, that is stretched over a series of rollers. In contrast, modular belts are composed of individual interlocking modules or links. Each module has built-in hinges or connecting rods that allow for easy assembly and disassembly. The modules are usually flat or slightly curved, and they can be customized with various surface patterns, textures, or accessories to meet specific application requirements.
- Flexibility:
Modular belts offer greater flexibility compared to traditional conveyor belts. The modular design allows for easy configuration and customization of the belt’s width, length, and layout. The interlocking modules can be added, removed, or repositioned as needed, enabling the creation of conveyor systems of different sizes and shapes. This flexibility makes modular belts adaptable to changing production processes or facility layouts, whereas traditional conveyor belts are relatively fixed in their dimensions and configurations.
- Load Distribution:
Modular belts distribute the load more evenly compared to traditional conveyor belts. The interlocking modules share the weight of the transported goods, reducing stress on individual components and enhancing the belt’s durability. In traditional conveyor belts, the load is concentrated on the belt’s surface, which can lead to uneven wear and potential damage. The load distribution capability of modular belts allows them to handle a wide range of loads, from lightweight packages to heavy bulk materials, with improved performance and longevity.
- Maintenance and Repair:
Maintenance and repair of modular belts are generally easier compared to traditional conveyor belts. If a module gets damaged or worn out, it can be replaced individually without the need to replace the entire belt. This modular replacement approach reduces downtime and maintenance costs. In contrast, repairing traditional conveyor belts often involves replacing a larger section or the entire belt, which can be more time-consuming and costly. Additionally, modular belts have a smooth and non-porous surface, making them easier to clean and resistant to debris or contaminants, enhancing hygiene and reducing maintenance requirements.
- Accumulation and Sorting:
Modular belts excel in accumulation and sorting applications. The interlocking modules create a flat and even surface that allows products to accumulate without interference. This feature is beneficial in assembly lines or distribution centers where items need to be temporarily stored or grouped before further processing or sorting. Traditional conveyor belts, on the other hand, may not provide the same level of product stability and accumulation capabilities.
- Tracking and Alignment:
Modular belts have excellent tracking and alignment characteristics. The interlocking modules ensure that the belt remains flat and stable during operation, minimizing the risk of tracking issues or belt misalignment. This accurate tracking improves overall system efficiency, reduces product spillage, and extends the life of the belt and other conveyor components. Traditional conveyor belts may require additional mechanisms or adjustments to maintain proper tracking and alignment.
- Specialized Applications:
Modular belts are suitable for a wide range of specialized applications. Their versatility and customizable design make them adaptable to specific material handling needs. For example, modular belts can withstand high temperatures, making them suitable for baking or heat-treatment applications where traditional belts may not be suitable. They can also be customized to provide tight transfers or small product gaps, which is beneficial in industries such as packaging. Traditional conveyor belts may not offer the same level of customization or specialized capabilities.
In summary, modular belts differ from traditional conveyor belts in terms of their design and functionality. The modular design and flexibility of modular belts allow for easy configuration, customization, and maintenance. They offer advantages such as improved load distribution, accurate tracking, and suitability for specialized applications. These differences contribute to the unique capabilities and benefits of modular belts in industrial settings.


editor by CX 2024-04-22